MAL-856 – a new game changer in immune-driven regeneration.
Using the unique immune modulatory mode of action of MAL-856 we target inflammatory disorders, restoring immune balance and advancing therapeutic applications.

Medical need.
Hair loss is highly prevalent and concerns approximately 70% of the world population. In a first step we focus on androgenetic alopecia (AGA), the hormone dependent male and female hair loss representing the main cause for hair thinning and baldness. Two medications (Minoxidil and Finasterid) with scientific proof of efficacy are presently available for treatment of this condition, but they merely increase the life span of “old” hairs and do not induce the growth of new ones. Moreover, they are effective only in a small fraction of affected people and have to be taken continuously for the rest of their lives. After stop of treatment the effect vanishes fast and hair loss reinitiates. Furthermore, especially Finasterid has been reported to cause severe side effects and since it interferes with the hormonal balance, it is only approved for men, not for women. Many studies have shown that people affected by hair loss suffer from a lower quality of life due reduced self-esteem, depression and suicidal thoughts. In contrast to the presently available medications, sCD83 demonstrably activates hair follicles and thus growth of new hair.
Product characteristics and immune modulatory activity of MAL-856.
MAL-856 is a structural variant of the extracellular domain of the membrane bound form of CD83 (mCD83). It is expressed in GMP quality as a recombinant protein in Pichia pastoris and subsequently purified using chromatography. MAL-856 is characterized by its anti-inflammatory properties inducing resolution of inflammation as previously demonstrated in specific pre-clinical autoimmune as well as transplantation models with sCD83. Interestingly, its application reduced inflammatory disease symptoms and enhanced allograft survival not only in preventive settings but also if applied therapeutically (Grosche et al., Front. Immunol.: 2020; Peckert-Maier et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci.: 2022, Peckert-Maier et al., Am. J. Transplant.: 2022). In addition, in a recent report we demonstrated for the first time that this protein also improves and accelerates wound healing processes in vivo (Royzman et al., Front. Immunol. 2022).
Preclinical in vivo studies: sCD83 boosts hair growth pathways.
Using an in vivo wound model in combination with transcriptome analyses we identified that pathways associated with hair growth and hair follicle development were induced in the presence of sCD83. This prompted us to investigate these findings in more detail and discovered that sCD83 accelerated hair regrowth.
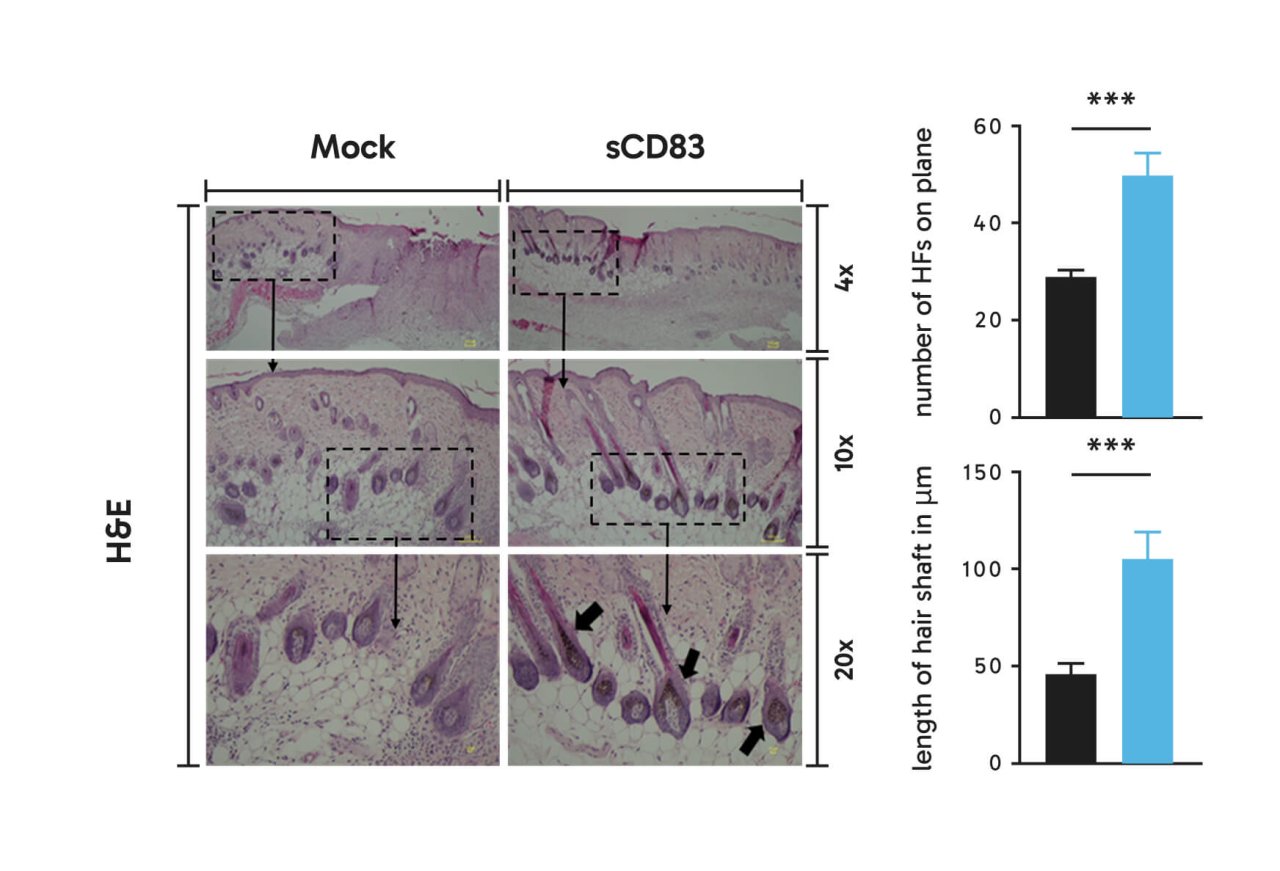
Preclinical in vivo studies: sCD83 induces hair follicle formation.
Moreover, using an epilation model, sCD83 treatment increased the number of hair follicles as well as the length of the hair shaft when compared to mock treated control animals (Figure on the left, Hair regrowth is boosted in sCD83-treated mice.).
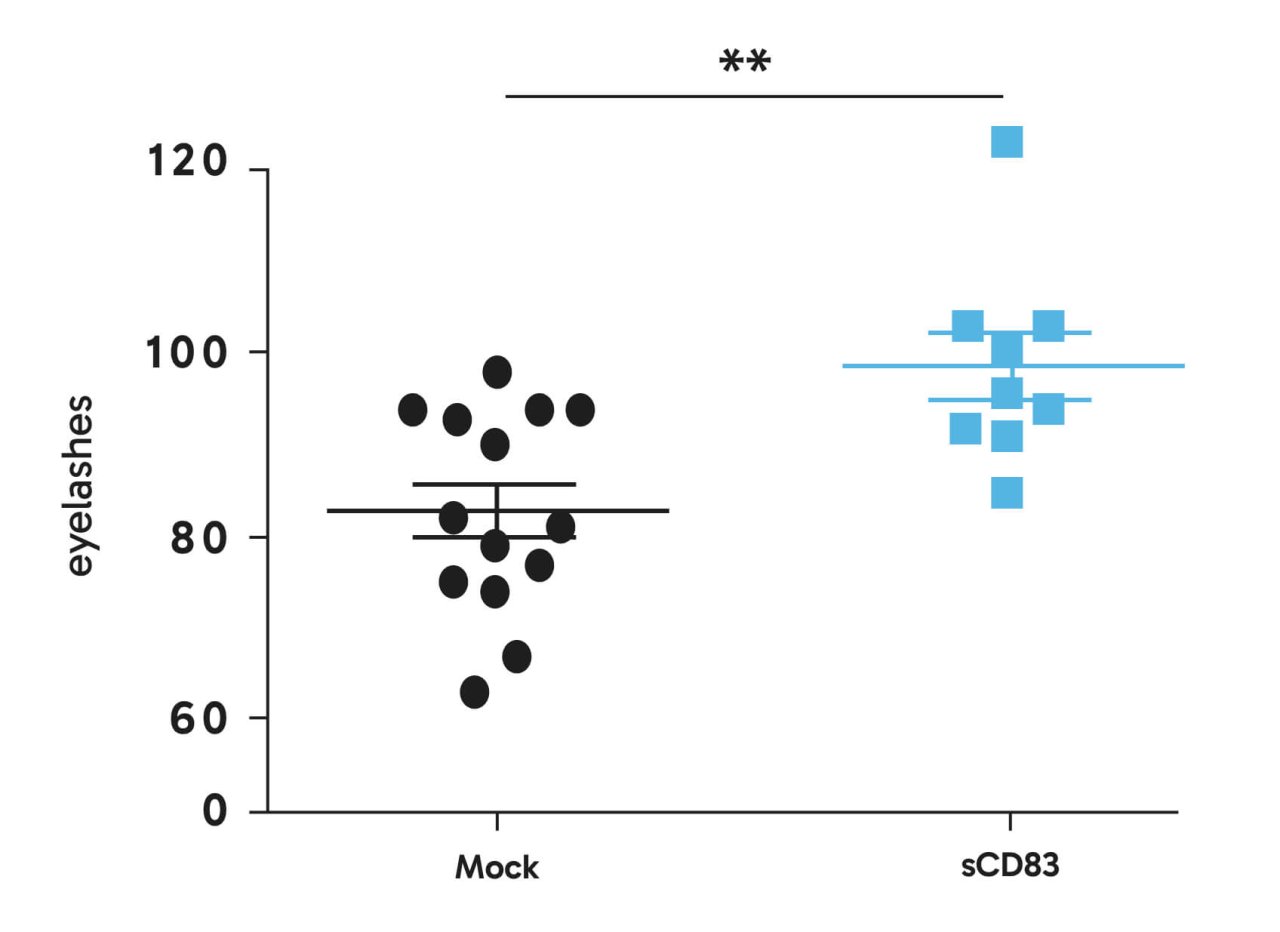
Preclinical in vivo studies: Topical sCD83 application increases the number and length of eyelashes
We investigated if topical administration of sCD83 modulates the number of eyelashes. Noteworthy, the sCD83-treated group revealed increased numbers of eyelashes with a longer and thicker shape when compared with PBS mock-controls (Figure on the left: Topical sCD83 application increases the number and length of eyelashes after topical application).
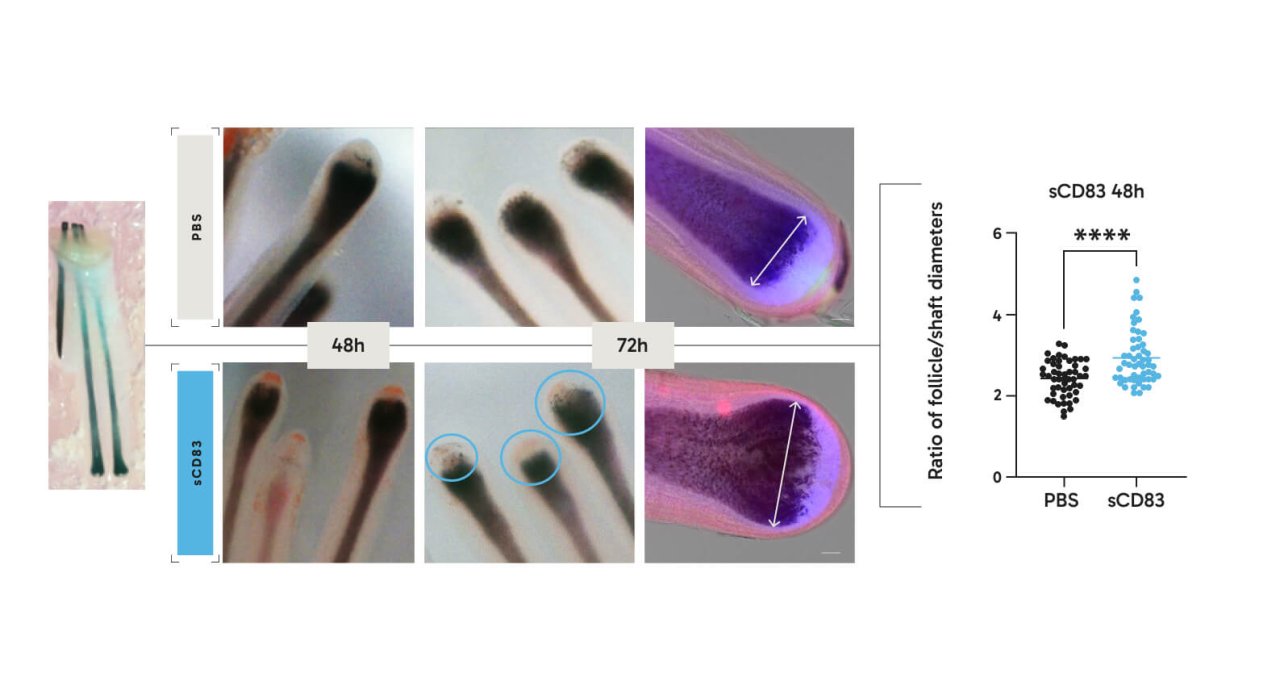
Human hair follicles: Our product prolongs the growing anagen phase
In order to translate our preclinical data into the human system, experiments were carried out using human hair follicles which were either incubated in vitro with sCD83 or as a control with PBS for 48 and 72 hrs, respectively. As shown in the Figure, hair follicles which were treated with PBS progressed already towards hair growth arrest (i.e. catagen-phase), while sCD83 treated hair follicles were still in the growing anagen phase as amongst others shown by a statistically highly significant larger diameter of the dermal papilla. This clearly indicates that sCD83 also boosts hair growth in a human setting.
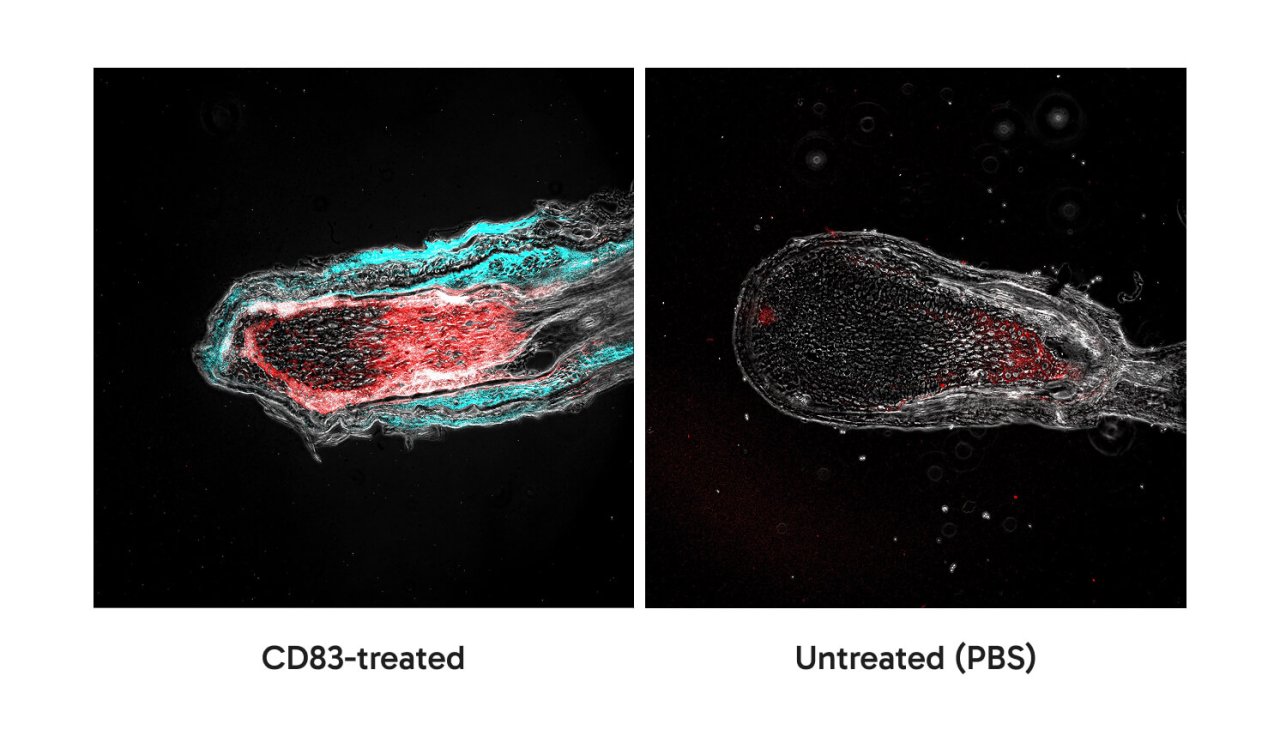
Human hair follicles: Our product inhibits cells death via the induction of anti-apoptotic molecules.
Human hair follicles incubated with our product or PBS as a control were immunohistochemically analyzed. As shown in the Figure on the left, human hair follicles treated with our product highly overexpress anti-apoptotic molecules such as BCL2 and MCL2, which inhibit cell death. In sharp contrast, human hair follicles treated with our product highly overexpress anti-apoptotic molecules such as BCL2 and MCL2, which inhibit cell death. As consequence, this leads to the prolongation of the anagen growing phase of hair follicles.
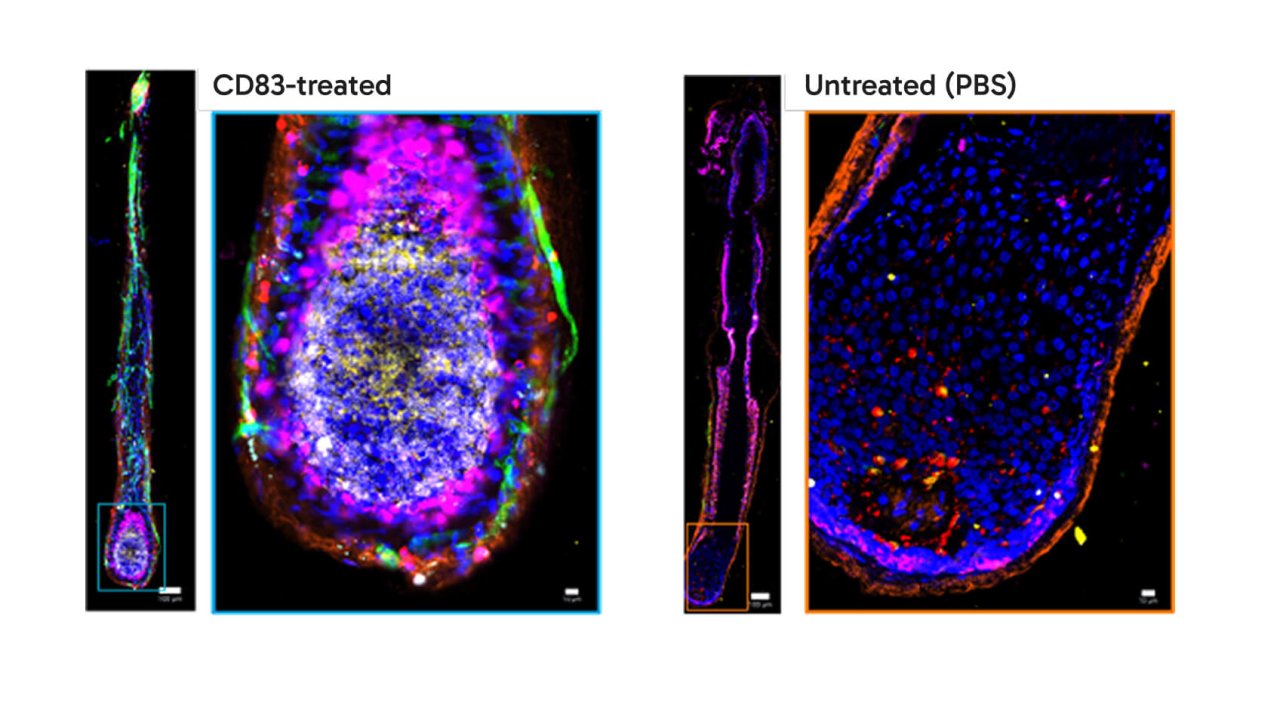
Human hair follicles: Our product inhibits apoptosis, induces cell proliferation, activates stem cells, and simultaneously induces keratin production
Human hair follicles were either incubated with sCD83 or PBS as a control and immunohistochemically analyzed using the latest MACSimaTM technology. Interestingly, our product induces specific molecules that are essential for stem cell activation (CD44), the prevention of cell death (MCL1) and keratin formation, such as cytokeratin 5 (an important building block of the hair thread) (left image). In sharp contast, in PBS-treated controls, these molecules were either induced only at a very low level or not at all (right image). The cell nucleus was stained with DAPI.
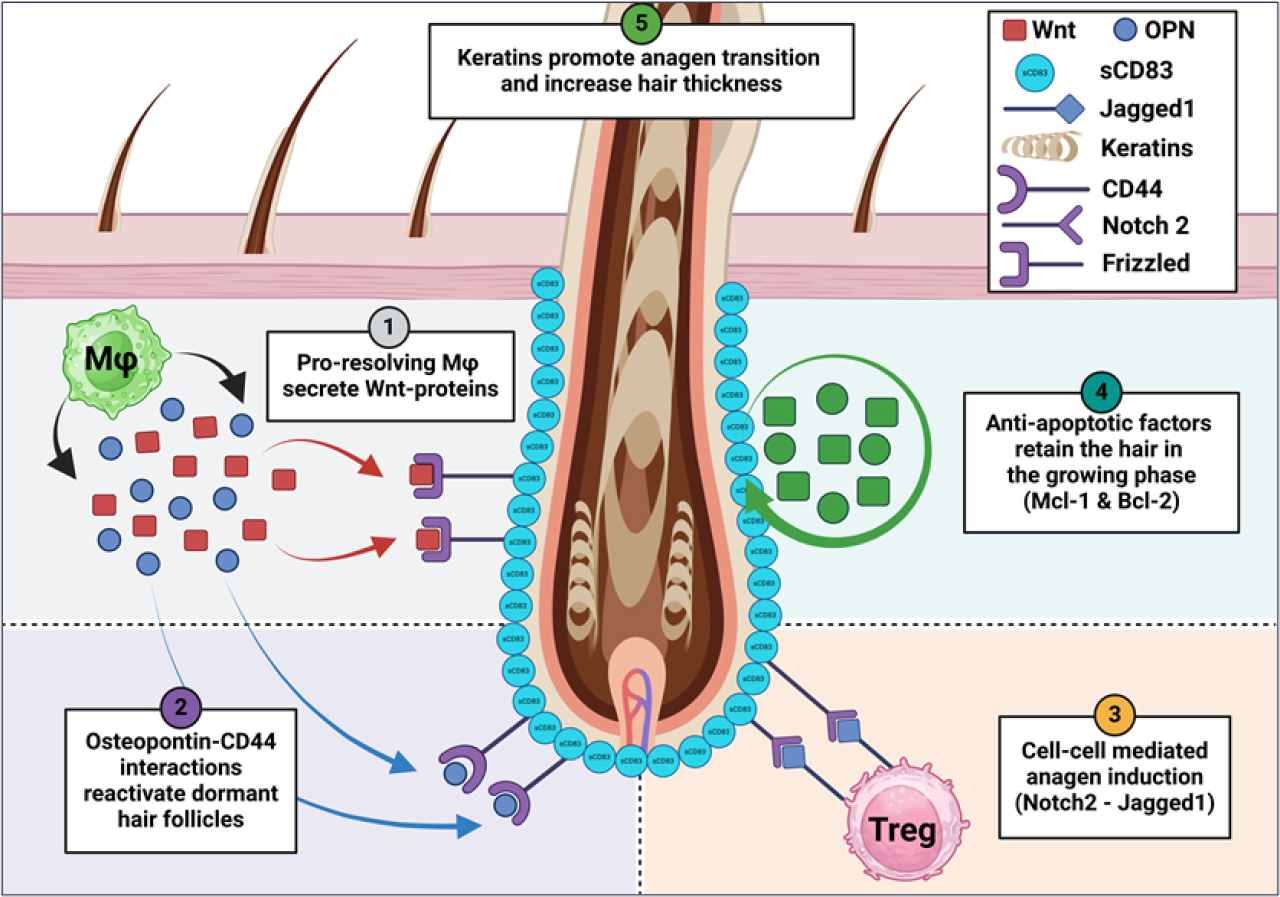
Mode of Action.
Preclinical in vivo models as well as human in vitro studies with human hair follicles revealed that our product is characterized by a synergistic multifactorial mode of action which finally leads to the activation of hair follicles and thus hair growth. The key features are summarized below:
• Inhibition of cell death, thereby prolonging the anagen growing phase of hair follicles
• Blocking of inflammation and thus, restoration of the immune privilege of the hair follicles
• Activation of hair follicle stem cells leading to hair growth
• Induction of Tregs which directly activate hair follicles
• Upregulation of keratins expression, the building blocks of hair
How does our product interfere with pathogenic mechanisms associated with androgenetic hair loss?
Androgenetic hair loss is mainly due to genetic factors and a degradation product of the hormone testosterone, i.e. dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT induces cell death in hair follicle which subsequently results in an inflammatory milieu, shortening and inhibition of the growing anagen phase, a miniaturization of hair follicles which are not able to produce strong hair threads anymore and finally die, leading to baldness.
Our product inhibits DHT-induced cell death, blocks inflammation, and restores the immune privilege of the hair follicles.
- It activates the growig anagen phase.
- It induces regulatory T cells which have been shown to directly interact with hair follicle stem cells, thereby activating them.
- It activates follicular stem cells, thereby stimulating hair growth.
- It induces the expression of keratins, which are the building blocks of hair.
How does our product interfere with immune mediated pathogenic mechanisms of alopecia areata?
In contrast to the hormone induced androgenetic hair loss, the second most common form of hair loss, alopecia areata, is an immune mediated hair loss disorder. Since we have previously shown that sCD83 strongly prevents autoimmune disorders in several preclinical models in vivo, including those for MS, RA and IBD, MAL-856 represents an ideal candidate also for the treatment of immune mediated alopecia areata, since it:
- Blocks inflammation and restores the immune privilege of hair follicles
- Induces Tregs, which inhibit follicle destroying effector T cells and thus the cause for AA
- Inhibits cells death of hair follicles and thus prolongs the growing anagen phase
- Activates cell proliferation and hair follicle stem cells
- Induces the expression of keratins, the building blocks of hair
Effects on hair follicles derived from androgenic alopecia patients.
Hair follicles derived from patients with androgenic alopecia are typically miniaturized and show only limited pigmentation. Their microenvironment is characterized by an overexpression of molecules linked to dihydrotestosteron (DHT)-induced hair loss and impaired stem cell function. In our studies, incubation of these follicles with our product led to a clear reduction of the expression of hair loss–associated factors. At the same time transcripts essential for hair growth were significantly upregulated in the treated samples. These findings provide strong support for our approach to develop MAL-856 as a novel therapeutic option for individuals affected by androgenetic alopecia.
IP protection
European patent granted in May 2025 (Appl./Patent No. 21717933.2 - 1109 / 4135745). Aditional patent applications have been filed in other countries including USA, Canada and Japan. Examinations are currently ongoing.